IT outsourcing is characterised by the existence of three elements – the service provider, the service recipient and their relationship.
As the importance of technology and IT services grows, so does the IT governance. This article will briefly present to you the IT governance factors relating to the three elements of outsourcing. It will also present a practical example of a service provider’s IT governance structure, based on that of Future Processing.
What is IT governance?
IT governance (ITG) may be considered a part of corporate governance – an organisational system of rules, processes and procedures by which a business is steered in order to attain its objectives. IT governance is defined as processes that safeguard an effective use of IT to support these business objectives. IT governance can be affected by a number of factors, including communication, trust, culture, as well as laws and regulations. Its systems can be set up with help of several frameworks, such as ISO27001. Good IT governance is the responsibility of both the service provider and the service recipient, however it is the latter that holds final responsibility.
IT governance factors
As discussed, there are separate IT governance factors that relate to each element of outsourcing: the service provider, the service recipient and their outsourcing relationship.
- IT governance factors for the service recipient
In order to effectively control your outsourcing relationship, as a service recipient, you require to have the following in place: a clear IT strategy, a chief information officer (CIO)/a director responsible for the strategy and IT managers supporting them. These will help to ensure alignment and integration of IT and business and that the IT needs of your business are met by the service provider.
- IT governance factors for the service provider
A governance structure of an IT service provider should be set up to ensure they can best meet the needs of their clients. The governance factors of the service providers include: an established market position, availability of IT expertise, a front office (client relationship management) and a back office (responsible for the actual delivery of the service). Ensuring these factors are met will allow your service provider to help guarantee a continued delivery of your services.
- IT governance factors for the outsourcing relationship
Factors concerning the relationship are factors concerning both the supplier and the client. These include: clearly defined roles in your relationship, unambiguous contracts (stating responsibilities, describing services to be provided and procedures for situations not covered by the contract and for price changes), steering organisations (meetings) on all levels (operational, tactical and strategic) and finally, trust in the partnership.
Case Study
IT Governance at Future Processing
Background
Future Processing is an IT services provider with an established market position: since 2000, we have been delivering software development services and solutions to clients across the industries, in Europe and beyond. Our team has grown from two people into a team of over 900 IT experts and enthusiasts of the latest IT technologies.
This long standing experience has taught us the value of trust, communication and relationships between partners – both on the level of individuals, and on the level of cooperation between two companies.
Figures show that our clients trust us – over 70% of our revenue comes from clients who have been with us for over 3 years and over 20% from clients that have used our services for 1-3 years.
Governance structure
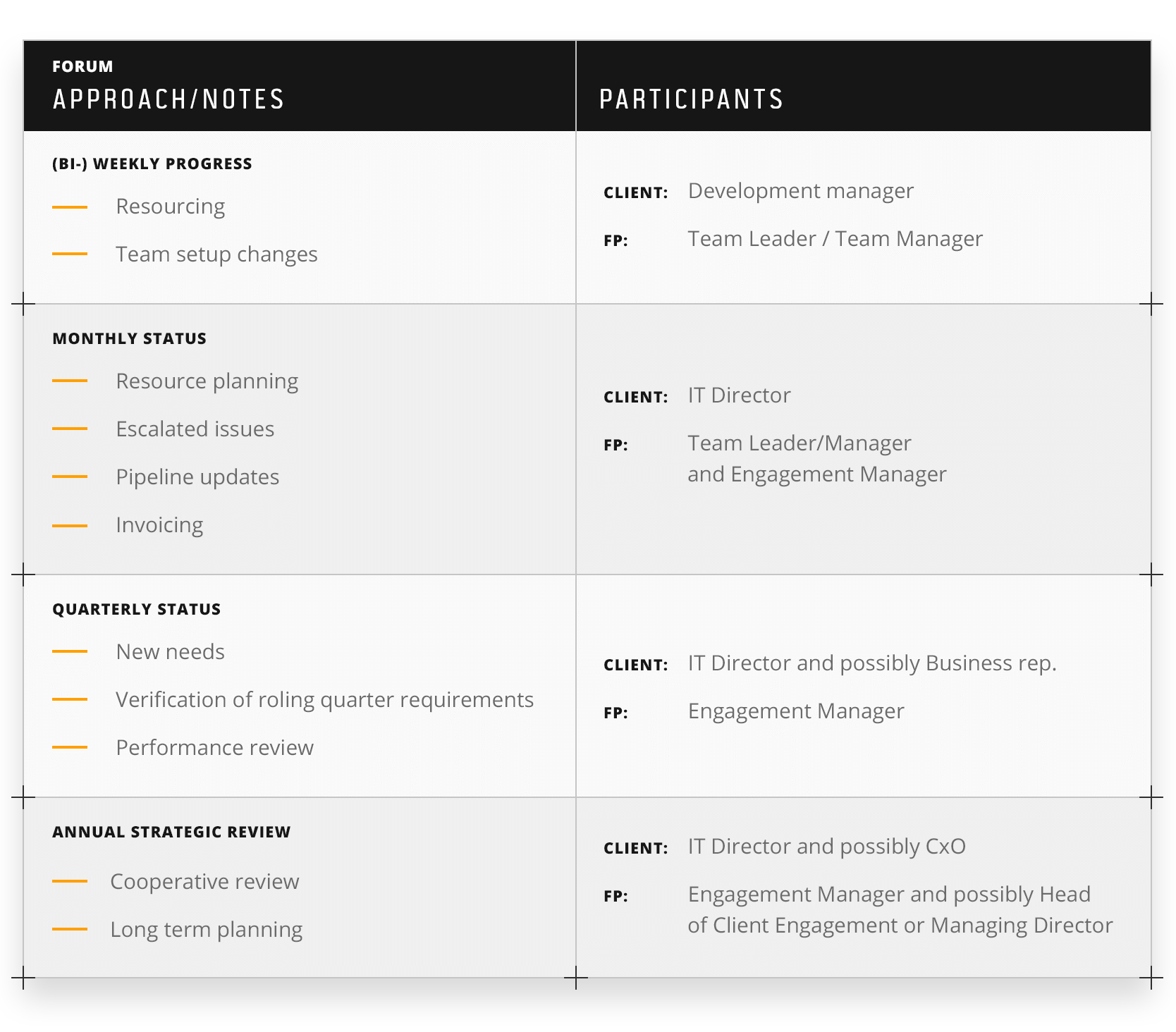
We have a defined governance structure and forums to support communication, on operational, tactical and strategic levels. This allows us to support relationships with our clients through a number of ways, including helping us to spot issues early, act proactively, report in a timely manner and at an appropriate level of authority, and have a solid, shared plan in mind.
We are ISO 27001:2013-certified which gives our clients an increased level of trust that their data is managed in a secure manner.
Governance structure at Future Processing
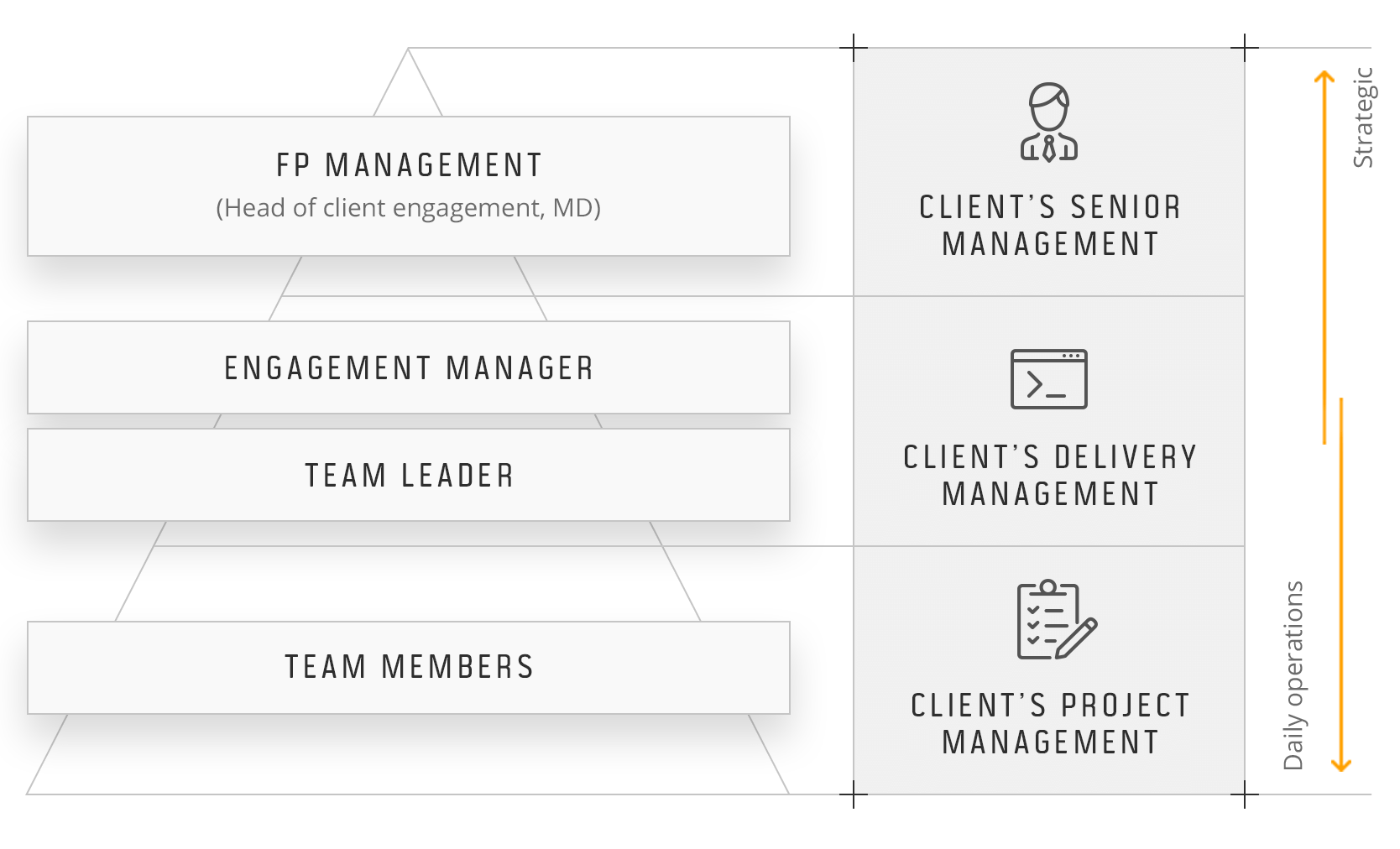
At the level of client relationships, our teams have been divided into front office (e.g. Client Engagement Managers) and back office (Delivery Teams) with clearly defined roles.
Example roles at Future Processing:
Client Engagement Manager
A Client Engagement Manager (CEM) is responsible for engaging in and developing the relationship with Future Processing’s clients.
A CEM actively searches for opportunities for Future Processing to become a more valuable Technology Partner for the client. This might be achieved by early identifying a need for adding, removing or adjusting services delivered and exploring new business models. A CEM is also encouraged to explore the customer market to acquire a deeper understanding of possible needs even before they arise.
Further to this, A CEM’s role is to monitor, negotiate and adjust the service level for ongoing work including, but not limited to, contract and rates table negotiation.
On a formal side, a CEM is expected to take care of the invoicing process and undertake a governance/oversight role for the client delivery teams, but is not involved with activities on a day-to-day basis (this role is performed by a Team Leader/ Scrum Master).
Team Leader / Scrum Master
While Team Leader is the traditional Future Processing title used in various contexts, the Scrum Master title is used in teams working in Scrum implying additional skills in Agile methodologies.
Key responsibility of the Scrum Master is to ensure proper implementation of the Scrum Framework and improve the team’s productivity by applying best industry practices and patterns and adjusting it when needed. A Scrum Master is accountable for the team process.
Additionally, within Future Processing, the Scrum Master is accountable for line management activities like monitoring absence, setting annual training plans and evaluations. A Scrum Master should also serve as the first escalation point for all the issues related to the work performed by his team or deliverables. This role is not present in Body Leasing model.
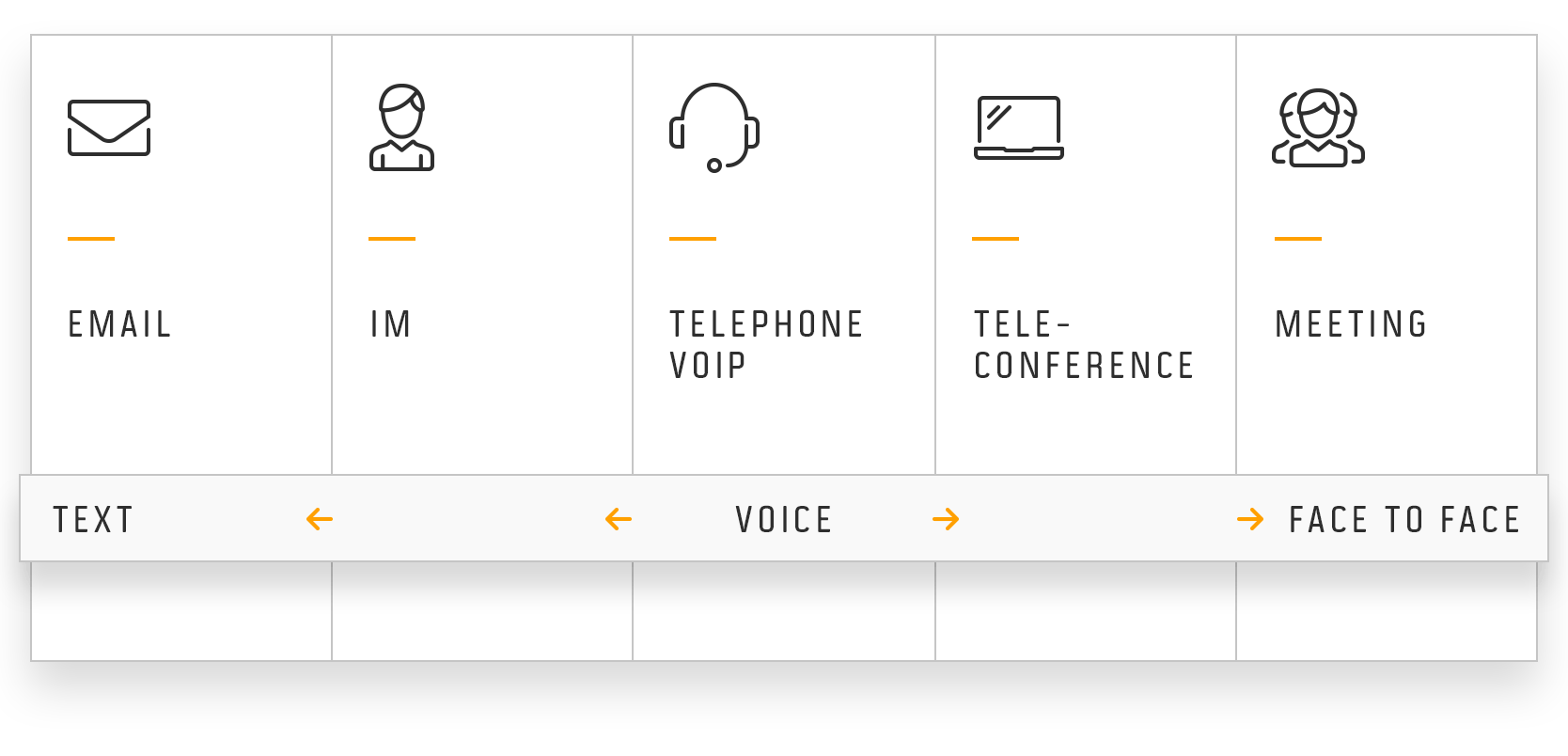
To ensure dialogue and regular communication with our clients, we propose the following forums and communication channels, which are flexible depending on our client’s and each project needs:
Governance forums at Future Processing
Communication channels at Future Processing
Conclusion
Why is IT governance important?
Working with an IT service provider can be a challenge, especially due to distance and split project teams. This is where appropriate IT governance plays its role. IT governance, backed up by solid corporate governance, should result in realising mutually agreed goals of the outsourcing partners. The governance is crucial to ensuring that a client’s technology strategy is aligned with their business strategy. To ensure this, Future Processing offers flexibility in its approach to governance.
Source: Beulen, E., Ribbers, P. and Roos, J. (2011) ‘Managing IT Outsourcing’, London: Routledge